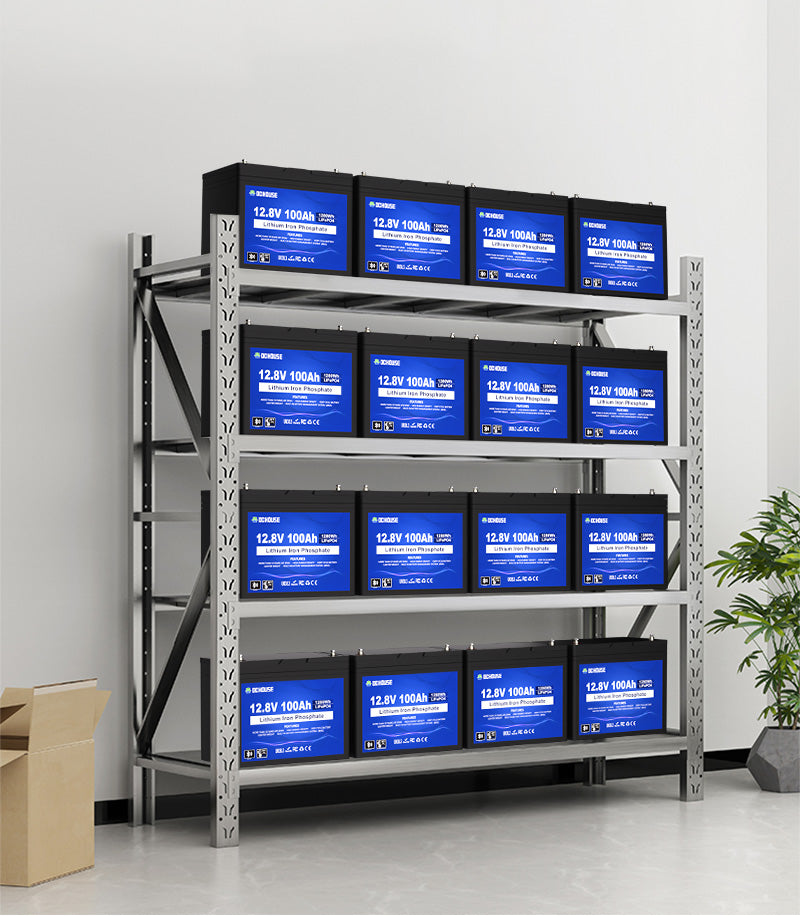
How to Store lithium Batteries
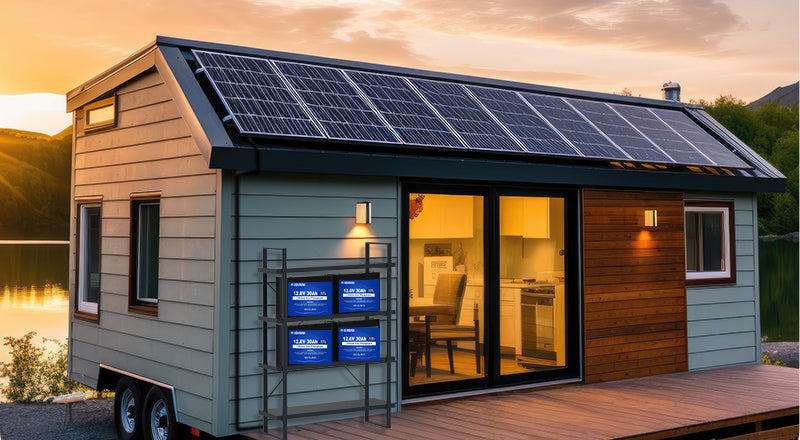

How should I store my lithium batteries ?

My cart 0 ithems
Others also bought

12V 12Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 50Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 100Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 200Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 100Ah 3.0 Portable Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Bluetooth & Low Temp Protection Battery

12V 100Ah 2.0 Portable Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 100Ah Portable Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 50Ah Portable Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Lithium Battery

12V 100Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Bluetooth & Low Temp Protection Battery

12V 165Ah Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Bluetooth & Low Temp Protection Battery


